Diagnosing and Treating High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common health issue that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It often develops gradually and can persist without noticeable symptoms. Hypertension increases the risk of severe health complications, such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems. Understanding this condition, its causes, and how it is diagnosed and managed by internal medicine can empower individuals to maintain better overall health.
What Is High Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure measures the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps blood throughout the body. High blood pressure occurs when this force remains consistently elevated, leading the heart and blood vessels to work harder than they should over time. Normal blood pressure usually hovers around 120/80 mmHg. When readings regularly exceed 130/80 mmHg, it can indicate hypertension, which falls into different categories based on severity. Routine monitoring is often the best way to detect if blood pressure levels rise above the healthy range.
What Causes It?
High blood pressure develops from a wide range of underlying factors. These can include lifestyle choices, genetic predispositions, or medical conditions. Although each individual’s situation differs, common contributors to high blood pressure include:
- Lifestyle Factors: Habitual behaviors such as consuming a diet high in sodium, chronic physical inactivity, smoking, and excessive alcohol intake play a significant role. These habits affect cardiovascular health and contribute to the development of hypertension over time.
- Age and Family History: Blood pressure tends to increase as people age, as arteries naturally stiffen and lose elasticity. Individuals with a family history of hypertension may have a heightened likelihood of developing the condition themselves.
- Medical Conditions and Medications: Certain health conditions, such as obesity or diabetes, are linked to an increased risk of developing high blood pressure.
- Stress: Ongoing stress or anxiety may contribute to temporary spikes in blood pressure levels.
How Is It Diagnosed and Treated?
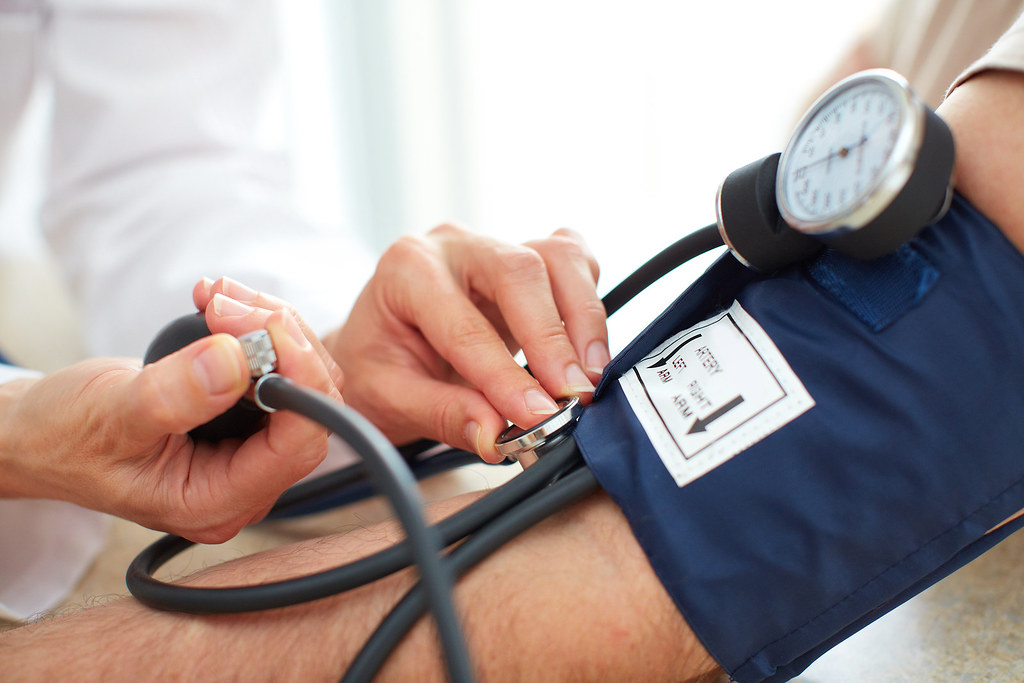
Diagnosing high blood pressure relies on consistent monitoring and accurate readings. A specialist in internal medicine typically uses a blood pressure cuff during routine checkups to assess whether an individual’s levels fall within a normal range. Because blood pressure can occasionally fluctuate due to temporary factors like stress or activity, sustained high readings across multiple appointments may be required before diagnosing hypertension. Standard blood pressure readings form the foundation of hypertension diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Once identified, high blood pressure treatment typically involves lifestyle modifications and, in some cases, prescribed medications. Non-medical solutions may be promoted first for situations where they may apply. Approaches may include:
- Dietary Changes: Adopting a healthy diet helps reduce sodium and increase nutrient-rich food intake. This assists in better blood pressure regulation.
- Physical Activity: Regular aerobic exercise strengthens the heart and improves blood circulation, contributing to improved blood pressure control.
- Avoidance of Smoking and Alcohol Limitation: Avoiding tobacco products entirely and reducing alcohol intake to moderate levels can yield measurable improvements in blood pressure.
- Medication Management: Physicians may prescribe medications such as diuretics, ACE inhibitors, or beta-blockers to help control blood pressure.
Consult an Internal Medicine Specialist
Regular monitoring, early diagnosis, and a targeted treatment approach remain key in addressing high blood pressure effectively. By focusing on manageable lifestyle adjustments and seeking support from medical professionals, patients can reduce risks and improve their overall well-being. Scheduling an appointment with an internal medicine specialist offers a reliable pathway to manage blood pressure effectively.
- What to Expect When Visiting a Foot and Ankle Specialist
- Causes of PTSD
- The Link Between Plantar Fasciitis and Weight Gain: What You Need to Know
- How Pet Ownership Can Positively Impact Life with Fibromyalgia
- The Importance of Stretching and Flexibility in Sports Medicine
Dr. Emma Green is a health and wellness expert with over 10 years of experience in nutrition and fitness. Passionate about helping others live their healthiest lives, Dr. Green shares practical advice on wellness, nutrition, and sustainable living through LivingSpristine.