What Causes Gout and How Do I Treat It?
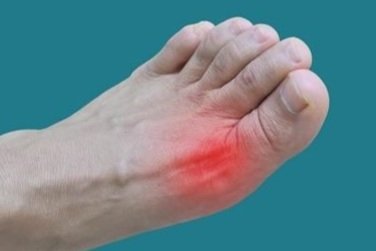
Gout is a complex condition that causes significant discomfort and impacts a person’s mobility. It is characterized by sudden and severe episodes of pain, often in the joints, accompanied by redness, swelling, and inflammation. Left untreated, gout can lead to long-term joint damage and other health complications. Understanding its causes and potential treatments is beneficial for managing this condition effectively and improving quality of life.
Causes Behind Gout Development
Gout primarily occurs when there is an excessive buildup of uric acid in the bloodstream. This condition, known as hyperuricemia, leads to the formation of sharp, needle-like crystals in the joints, which trigger intense pain and inflammation. Uric acid is a natural waste product formed in the body when purines, found in certain foods and drinks, break down. While most uric acid is eliminated through urine, excessive production or insufficient elimination can result in its accumulation.
Several factors contribute to hyperuricemia, including dietary habits, lifestyle choices, and genetic predisposition. Consuming high-purine foods such as red meat, organ meats, and certain types of seafood, as well as drinking alcohol and consuming sugary beverages, can elevate uric acid levels. Additionally, conditions like obesity, chronic kidney disease, and metabolic syndrome may impair the body’s ability to flush out uric acid efficiently. Family history also plays a role, as genetic markers associated with gout risk can affect how the body regulates uric acid.
Symptoms That Signal Gout
Recognizing the symptoms of gout is key to seeking timely intervention. Common indicators include:
- Sudden, severe pain, often at night
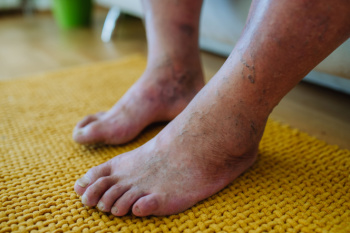
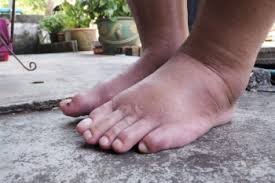
- Swelling and redness in the affected joint
- Warmth or tenderness in the area
- Limited joint mobility during flare-ups
- Recurrent episodes after periods of remission
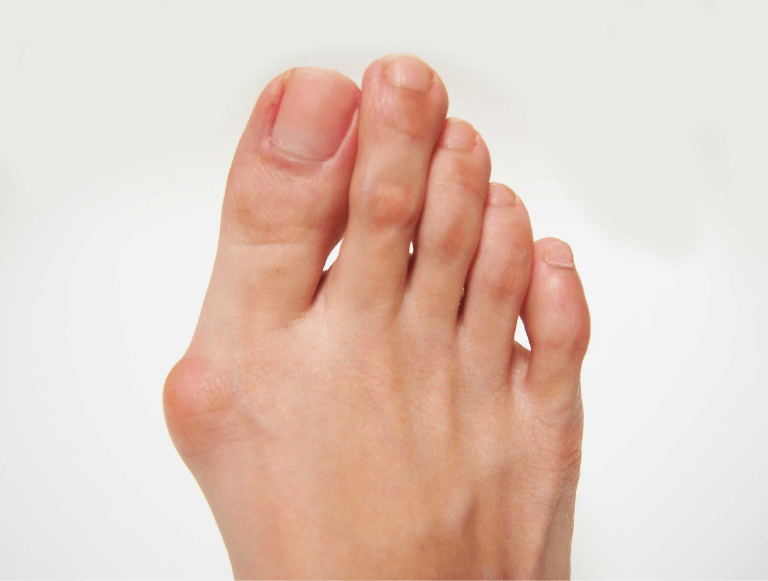
Gout can affect any joint, but it most commonly manifests in the big toe. Individuals experiencing these symptoms should consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and management.
Treatments That Address Gout
The treatment of gout focuses on alleviating pain during flare-ups, reducing inflammation, and preventing future episodes. This often involves a combination of medications and lifestyle changes. By addressing both symptoms and underlying causes, treatment can help manage the condition effectively.
Medications like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, or colchicine can provide quick relief during acute attacks. Long-term therapies target uric acid levels by reducing its production or enhancing its excretion. These treatments are typically recommended based on the severity and frequency of a person’s gout episodes.
Lifestyle changes are just as significant in managing gout. Limiting purine-rich foods, reducing alcohol intake, and staying hydrated can lower uric acid levels. Maintaining a healthy weight and staying active can further reduce the risk of future complications.
Start Your Gout Treatment Journey Today
Managing gout requires a combination of medical guidance and consistent lifestyle changes. Recognizing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is the first step toward minimizing its impact on your life. If you’re noticing warning signs of gout, seeking professional advice can help you build an effective plan to alleviate symptoms and prevent future flare-ups. Take control of your health today and explore solutions that work for your needs.
- What to Expect When Visiting a Foot and Ankle Specialist
- Causes of PTSD
- The Link Between Plantar Fasciitis and Weight Gain: What You Need to Know
- How Pet Ownership Can Positively Impact Life with Fibromyalgia
- The Importance of Stretching and Flexibility in Sports Medicine
Dr. Emma Green is a health and wellness expert with over 10 years of experience in nutrition and fitness. Passionate about helping others live their healthiest lives, Dr. Green shares practical advice on wellness, nutrition, and sustainable living through LivingSpristine.