The Role of Sports Medicine in Injury Recovery and Performance
Recovering from an injury involves more than just rest. Athletes—whether competitive or recreational—require focused care that promotes healing while helping maintain strength, mobility, and long-term function. Sports medicine offers a specialized approach to treating injuries related to movement, impact, and overuse. This field combines diagnostics, treatment, and rehabilitation strategies to address the unique needs of physically active individuals. The goal is not only to restore health but to support a safe and sustainable return to activity.
Diagnosing Movement-Related Injuries
Sports medicine specialists evaluate injuries through a detailed physical exam, medical history, and diagnostic imaging when needed. The focus is on understanding how the injury occurred and how movement patterns may have contributed to it. Common conditions treated include sprains, ligament tears, muscle strains, tendonitis, and joint instability. By identifying the precise tissue or system affected, providers create treatment plans tailored to the demands of the athlete’s sport or fitness routine. Early and accurate diagnosis helps guide recovery and limits unnecessary downtime.
Reducing pain and swelling is often the first step in recovery. Ice, compression, elevation, and brief rest are typically used in the acute phase. In some cases, providers may recommend anti-inflammatory medications or therapeutic modalities such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation. These methods work together to calm the injured area while maintaining as much mobility as possible. Sports medicine professionals monitor progress closely, making adjustments as the injury begins to heal.
Individualized Rehabilitation Programs
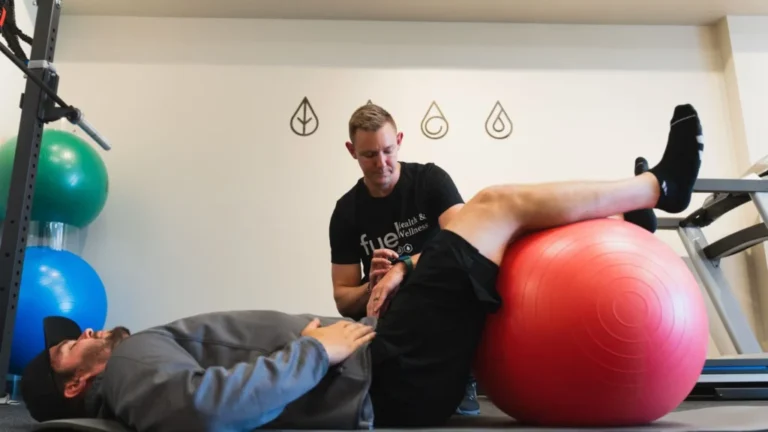
Each recovery plan reflects the specific injury, sport, and individual’s goals. Sports medicine teams—including physicians, physical therapists, and athletic trainers—develop targeted rehabilitation plans to rebuild strength, range of motion, and balance. Early-stage exercises help restore basic function, while later phases introduce sport-specific movements to prepare the body for return to competition. Careful progression helps reduce the risk of reinjury and supports full functional recovery.
Performance Optimization During Recovery
Even while healing, athletes can often maintain elements of their training with support from a sports medicine team. Cross-training, modified workouts, and alternative conditioning methods help preserve cardiovascular fitness and muscular endurance. This approach not only shortens the gap between injury and return but also keeps athletes mentally engaged during recovery. Working with knowledgeable professionals allows individuals to adapt their training safely without delaying healing.
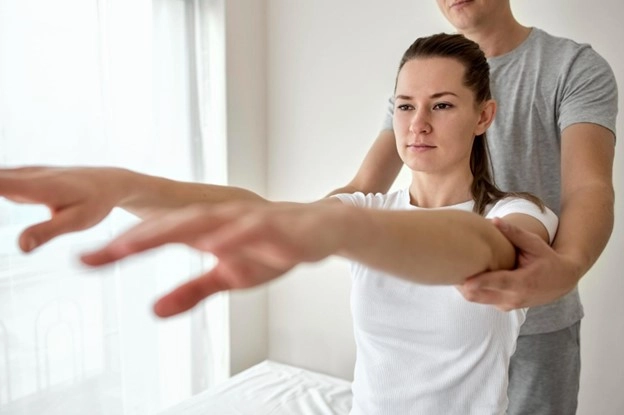
Sports medicine plays a key role in identifying risk factors that may contribute to future injuries. Poor biomechanics, muscular imbalances, and incorrect technique can place repeated stress on joints and tissues. Through movement analysis, gait evaluation, and strength assessments, providers pinpoint areas of vulnerability. Recommendations may include changes in training routines, stretching techniques, or strengthening exercises. These preventive measures support more durable movement patterns and reduce the likelihood of recurring injuries.
While many sports injuries respond to conservative care, others may require surgical treatment. Sports physicians coordinate care with orthopedic surgeons when structural damage—such as ligament tears or fractures—warrants operative repair. Following surgery, rehabilitation remains central to restoring full function. The sports medicine team continues to guide progress and manage milestones on the path to recovery, emphasizing a safe and steady return to sport.
Visit a Sports Medicine Expert
Sports med extends beyond acute injuries to support lifelong athletic participation. Providers help manage chronic conditions such as tendon disorders, joint inflammation, and overuse injuries that develop gradually over time. They also assist athletes during transitions, whether returning from surgery, managing age-related changes, or adapting to new training goals. With ongoing guidance, individuals can continue participating in physical activity with greater comfort, efficiency, and confidence in their body’s capabilities.
- What to Expect When Visiting a Foot and Ankle Specialist
- Causes of PTSD
- The Link Between Plantar Fasciitis and Weight Gain: What You Need to Know
- How Pet Ownership Can Positively Impact Life with Fibromyalgia
- The Importance of Stretching and Flexibility in Sports Medicine
Dr. Emma Green is a health and wellness expert with over 10 years of experience in nutrition and fitness. Passionate about helping others live their healthiest lives, Dr. Green shares practical advice on wellness, nutrition, and sustainable living through LivingSpristine.