What is Eczema and How to Manage It
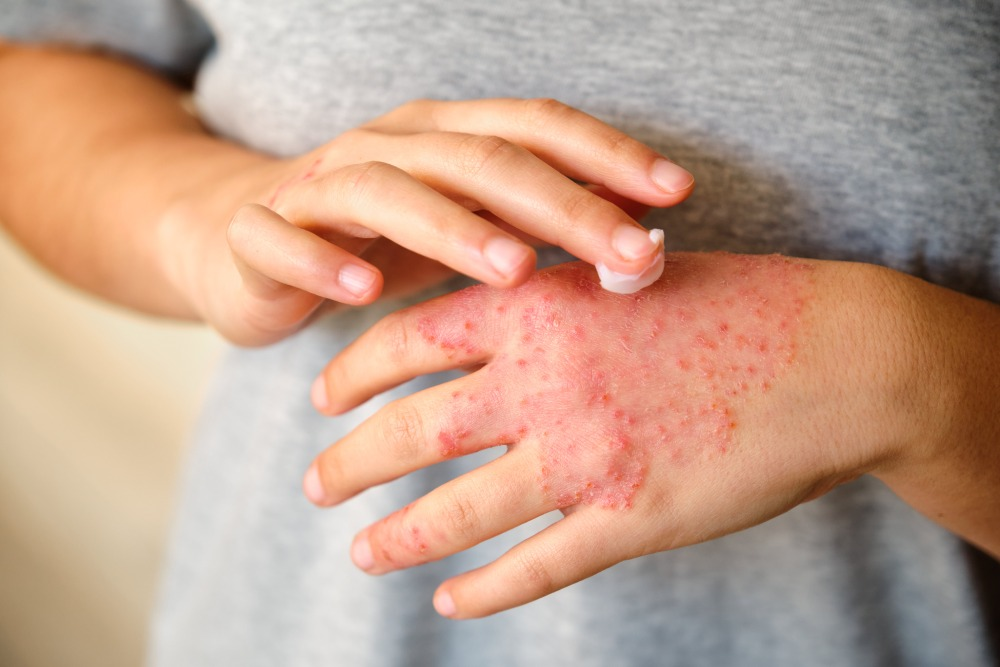
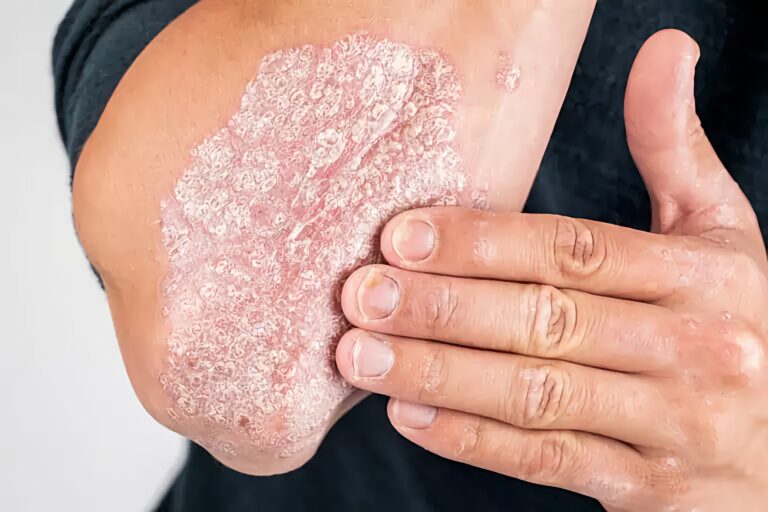
Eczema is a common skin condition that affects millions of people around the world. It can cause dry, itchy, red, and inflamed patches of skin, making everyday life uncomfortable and even painful. If you’re dealing with eczema or have a loved one who is, understanding what it is and how to manage it can make a big difference.
In this article, we’ll break down what eczema is, what causes it, the different types, and most importantly, how to manage and relieve the symptoms naturally and medically. We’ll also answer five frequently asked questions to help clear up any confusion.
What is Eczema?
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that makes the skin red, dry, and itchy. It can show up in different parts of the body and vary in severity from person to person.
Eczema isn’t contagious, which means you can’t catch it from someone else. However, it’s often linked to genetics, allergies, and problems with the immune system or skin barrier.
What Causes Eczema?
There’s no single cause of eczema. Instead, it’s usually triggered by a combination of factors:
1. Genetics
If eczema runs in your family, you’re more likely to develop it. Children of parents with eczema, asthma, or hay fever are especially at risk.
2. Immune System
People with eczema often have overactive immune systems. When the immune system reacts too strongly to irritants or allergens, it causes inflammation and itching.
3. Weak Skin Barrier
The skin barrier helps lock in moisture and keep out harmful substances. If this barrier is weak, skin becomes dry and prone to irritation.
4. Environmental Triggers
Things like:
- Soaps and detergents
- Certain fabrics (like wool)
- Dust mites
- Pet dander
- Pollen
- Heat and sweat
can all cause flare-ups in people with eczema.
Who Gets Eczema?
Eczema often begins in early childhood, but anyone can get it at any age. Many babies and toddlers develop it on their cheeks, arms, and legs. While some children outgrow it, others continue to have symptoms into adulthood.
Types of Eczema
There are several types of eczema. Here’s a quick overview:
| Type of Eczema | Description |
| Atopic Dermatitis | The most common type. Often starts in childhood. |
| Contact Dermatitis | Caused by touching irritants like soaps or chemicals. |
| Dyshidrotic Eczema | Causes small, itchy blisters on hands and feet. |
| Nummular Eczema | Round, coin-shaped spots on the skin. |
| Seborrheic Dermatitis | Affects oily areas like scalp, face, and chest. |
| Stasis Dermatitis | Occurs when blood flow is poor in the legs. |
How to Manage Eczema
Eczema doesn’t have a permanent cure, but managing symptoms is possible with the right care and lifestyle choices. Here are ways to help soothe and prevent flare-ups:
1. Moisturize Regularly
Hydrated skin is less likely to flare up. Use thick, fragrance-free moisturizers or ointments like petroleum jelly multiple times a day, especially after bathing.
2. Avoid Triggers
Identify and avoid things that cause your eczema to flare. Keep a journal to track your symptoms and what may have triggered them.
3. Use Gentle Skincare Products
Avoid soaps and cleansers with strong fragrances or alcohol. Choose products labeled “for sensitive skin” or “eczema-friendly.”
4. Take Short, Lukewarm Showers
Hot water dries out your skin. Keep showers short and use gentle cleansers. Pat your skin dry and apply moisturizer right after.
5. Wear Soft, Breathable Fabrics
Cotton clothes are best. Avoid wool or synthetic fabrics that irritate the skin.
6. Control Stress
Stress can trigger or worsen eczema. Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or gentle yoga.
7. Use Medications When Needed
Over-the-counter or prescription medications can help:
- Topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
- Antihistamines to relieve itching
- Antibiotics if there’s an infection
- Prescription creams that calm the immune system (like tacrolimus)
Always consult a healthcare provider before using medications.
Natural Remedies for Eczema
Some people find relief with natural options. While these aren’t cures, they may help ease symptoms:
– Coconut Oil
Has anti-inflammatory and moisturizing properties.
– Oatmeal Baths
Colloidal oatmeal can soothe and calm itchy skin.
– Aloe Vera Gel
Reduces redness and irritation.
– Sunflower Oil
Helps repair the skin barrier and reduce inflammation.
Make sure to patch-test any natural remedy first to see how your skin reacts.
Eczema Home Care Tips
- Use a humidifier in dry weather
- Keep nails trimmed to avoid scratching
- Wash new clothes before wearing
- Avoid smoking and second-hand smoke
- Keep the home free of dust and pet hair if you’re sensitive
Living with Eczema
Eczema can affect more than just your skin. It may impact your mental health, sleep, and confidence. Don’t hesitate to reach out to a doctor or dermatologist if you’re struggling to manage it. Support groups and therapy can also help with emotional stress linked to eczema.
Final Thoughts
Eczema is a long-term condition, but with the right care, it can be controlled and managed. Focus on keeping your skin moisturized, avoiding triggers, and working with a doctor when needed. Everyone’s eczema is different, so what works for one person might not work for another. Be patient and consistent with your skincare routine.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can eczema go away on its own?
Sometimes. In children, eczema may disappear with age. However, many people continue to experience it into adulthood, and it requires ongoing care.
2. Is eczema contagious?
No. Eczema is not an infection and cannot spread from person to person.
3. What foods trigger eczema?
Some people are sensitive to dairy, eggs, nuts, soy, or gluten. An elimination diet under medical supervision can help identify food triggers.
4. Is eczema caused by poor hygiene?
Not at all. Eczema is related to genetics, immune function, and skin barrier health—not cleanliness.
5. Can I cure eczema permanently?
There’s no permanent cure, but many people can manage it so well that symptoms rarely show up. Good skincare and avoiding triggers are key.
Dr. Emma Green is a health and wellness expert with over 10 years of experience in nutrition and fitness. Passionate about helping others live their healthiest lives, Dr. Green shares practical advice on wellness, nutrition, and sustainable living through LivingSpristine.