Pain Management Options for Easing the Effects of Sciatica

Sciatica is a prominent cause of pain that radiates from the lower back down through the leg. This condition may significantly impact daily activities and quality of life. Understanding the various pain management approaches available can help individuals work with healthcare professionals to develop effective treatment strategies.
What Is Sciatica?
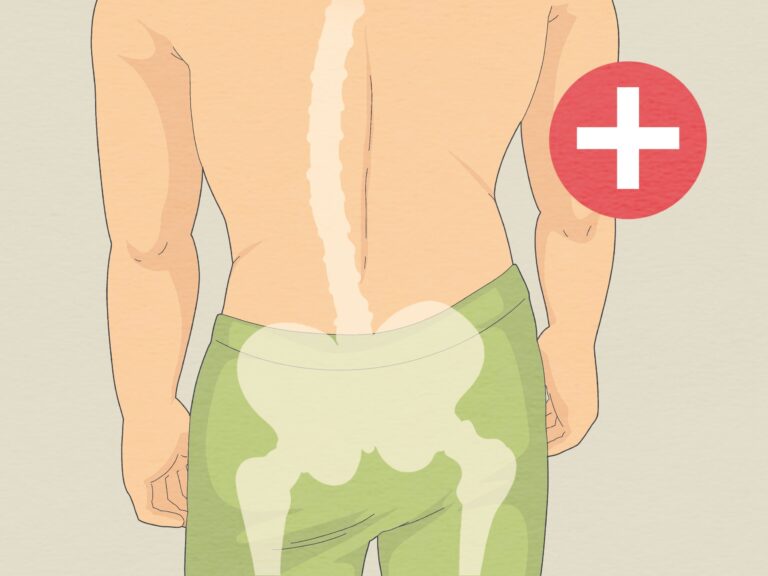
Sciatica refers to pain that travels along the path of the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back through the hips and buttocks and down each leg. The condition typically affects only one side of the body and can vary in intensity from mild discomfort to severe, debilitating pain. When this nerve becomes compressed or irritated, it can produce a range of symptoms beyond pain, including numbness, tingling, and weakness in the affected leg or foot. Sciatica symptoms often worsen when sitting or sneezing. The pain may feel sharp or burning and can extend from the lower back all the way down to the toes.
What Causes It?
Several underlying conditions lead to sciatica by compressing or irritating the sciatic nerve. Understanding these causes helps healthcare providers develop targeted treatment approaches. Conditions linked to sciatic symptoms include:
- Herniated Disc: A herniated disc occurs when the soft inner material of a spinal disc pushes through a crack in the tougher exterior casing. This displaced material can press against the sciatic nerve, causing pain and inflammation. Herniated discs are a leading cause of sciatica.
- Other Contributing Factors: Trauma from an injury, diabetes, or degenerative disc disease can also contribute to sciatic nerve compression or damage.
How Is It Managed?
Healthcare professionals may recommend various approaches to manage sciatica symptoms. Treatment plans are typically tailored to the individual’s specific condition, severity of symptoms, and underlying causes. Pain management plans can range from at-home lifestyle changes to proper medical intervention.
Conservative Treatment Options
Many individuals find relief through non-surgical approaches. Physical therapy helps strengthen supporting muscles and improve flexibility. Specific exercises may be recommended to reduce pressure on the sciatic nerve. The timing and duration of these treatments should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Advanced Treatment Options
For persistent symptoms that do not respond to conservative treatments, healthcare providers may recommend more advanced interventions and therapies. PRP injections directly to the affected area may aid the body’s healing processes. In severe cases where conservative treatments have not provided relief, surgical options may be discussed. These procedures aim to remove the source of nerve compression and are typically reserved for specific situations.
Lifestyle Modifications
Healthcare providers may recommend changes to daily activities and posture. Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce pressure on the spine and sciatic nerve. Regular, low-impact exercise may help strengthen the muscles that support the spine.
Seek Professional Pain Management Services
Sciatica can significantly impact quality of life, but various management options are available to help address symptoms. Each individual’s experience with sciatica is unique, and what works for one person may not be suitable for another. A comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare provider can help determine the most appropriate approach for your specific situation.
- What to Expect When Visiting a Foot and Ankle Specialist
- Causes of PTSD
- The Link Between Plantar Fasciitis and Weight Gain: What You Need to Know
- How Pet Ownership Can Positively Impact Life with Fibromyalgia
- The Importance of Stretching and Flexibility in Sports Medicine
Dr. Emma Green is a health and wellness expert with over 10 years of experience in nutrition and fitness. Passionate about helping others live their healthiest lives, Dr. Green shares practical advice on wellness, nutrition, and sustainable living through LivingSpristine.