3 Common Gynecological Procedures
Gynecological procedures play a valuable role in maintaining reproductive health and diagnosing or resolving health concerns. Understanding these procedures, their purposes, and what they entail can help individuals feel more prepared when discussing them with their healthcare providers. Here is more information on three commonly performed gynecology procedures:
Pap Smear
A Pap smear is a screening test in gynecology designed to detect abnormal cells in the cervix, which could indicate cervical cancer or other conditions. It is typically performed during routine gynecological exams. During the test, a healthcare provider collects a small sample of cells from the cervix using a swab, brush, or spatula. The sample will be sent to a laboratory for analysis.
A Pap smear does not diagnose cervical cancer but identifies abnormalities that warrant further investigation. Early detection through regular Pap smears can improve treatment outcomes by addressing any issues before they progress. It is common for individuals to receive Pap smear results within one to two weeks. If the test results indicate abnormalities, the next step may involve additional diagnostic procedures, such as a colposcopy or a biopsy.
Colposcopy
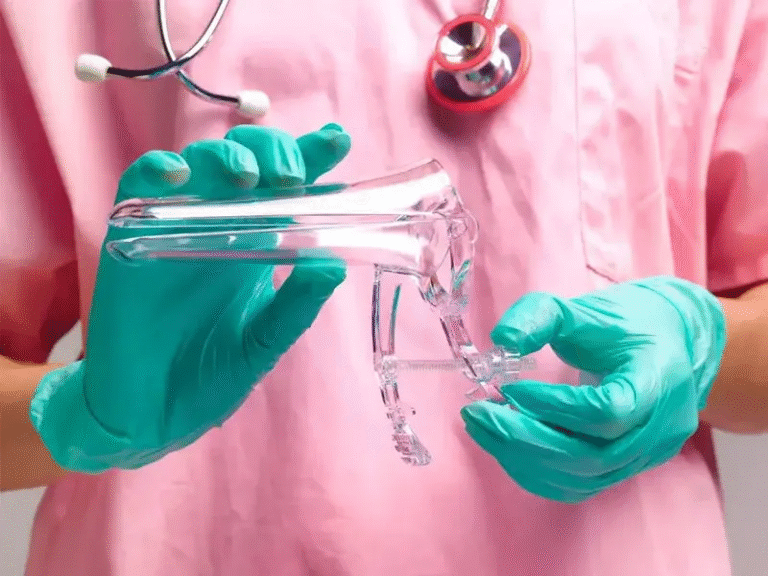
A colposcopy is a diagnostic procedure healthcare providers use to examine the cervix, vagina, and vulva for abnormal tissue. It is often recommended when a Pap smear yields abnormal results or when visible changes in the cervix are detected during an exam. This procedure involves using a colposcope, a device equipped with a light and magnification lens, to provide a detailed view of the tissue.
During the procedure, the healthcare provider may apply a solution to highlight abnormal areas. If suspicious tissue is identified, a small biopsy may be performed to collect a sample for laboratory testing. The procedure typically takes about 20 minutes and is performed in a healthcare provider’s office. Patients may experience mild discomfort but can generally resume normal activities afterward. Results from the colposcopy or biopsy usually take a few days to a week to be processed.
Endometrial Biopsy
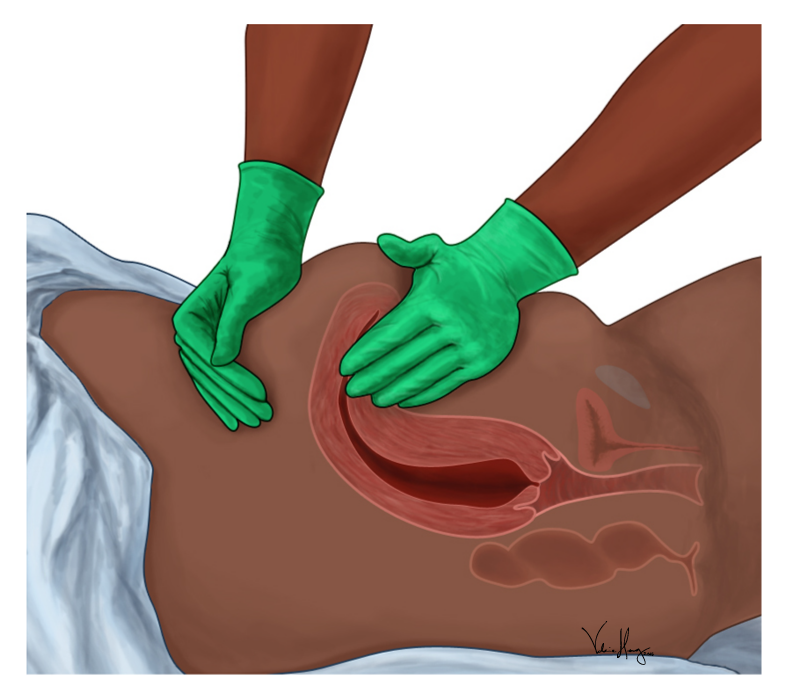
An endometrial biopsy is used to collect a tissue sample from the lining of the uterus, also known as the endometrium. This procedure helps diagnose issues such as abnormal uterine bleeding and hormonal imbalances. It can also identify conditions like endometrial hyperplasia or cancer. To perform an endometrial biopsy, a healthcare provider inserts a thin, flexible instrument through the cervix. This is used to gently remove a small portion of the uterine lining.
Patients may experience cramping during the procedure, but these sensations usually subside quickly. The sample is sent to a laboratory and analyzed to identify any unusual changes in the endometrial cells. These can provide insight into potential health concerns. Results are typically available within one to two weeks, and the findings guide the next steps in a care plan.
Find a Gynecology Professional
Gynecological procedures such as Pap smears, colposcopies, and endometrial biopsies are key components of reproductive healthcare. Each serves distinct purposes, from screening for cervical cancer to diagnosing underlying conditions. By familiarizing yourself with these procedures, you can engage in informed discussions with your healthcare provider to address any concerns. Consult with your provider for personalized advice and guidance tailored to your needs.
- What to Expect When Visiting a Foot and Ankle Specialist
- Causes of PTSD
- The Link Between Plantar Fasciitis and Weight Gain: What You Need to Know
- How Pet Ownership Can Positively Impact Life with Fibromyalgia
- The Importance of Stretching and Flexibility in Sports Medicine
Dr. Emma Green is a health and wellness expert with over 10 years of experience in nutrition and fitness. Passionate about helping others live their healthiest lives, Dr. Green shares practical advice on wellness, nutrition, and sustainable living through LivingSpristine.